
1. 1697번 숨바꼭질
1-1. 링크
1-2. 문제 해석
1-3. 코드 및 해설
1. 1697번 숨바꼭질
1-1. 링크
1697번: 숨바꼭질
수빈이는 동생과 숨바꼭질을 하고 있다. 수빈이는 현재 점 N(0 ≤ N ≤ 100,000)에 있고, 동생은 점 K(0 ≤ K ≤ 100,000)에 있다. 수빈이는 걷거나 순간이동을 할 수 있다. 만약, 수빈이의 위치가 X일
www.acmicpc.net
1-2. 문제 해석
BFS 문제인데 2차원이 아니라 그냥 x좌표만 있는 문제라고 보면 된다.
- 움직일 수 있는 방법이 -1, +1, *2 이렇게 3가지가 있다.
- 수빈이와 동생이 0과 100,000에도 서있을 수 있다는 점에 유의하자.
이 2가지만 신경 쓰면 쉽게 풀 수 있는 문제이다.
나는 두 번째 유의점을 신경 못써서 한참을 헤맸다 ㅠㅠ...
| 입력 | 출력 |
| 0 100000 | 22 |
| 100000 0 | 100000 |
출력이 잘 나오는데 계속 틀렸다고 뜬다면 위 두 입력에 대한 출력을 확인해보자.
1-3. 코드 및 해설
- HashSet 사용
public class Main {
static int N, K;
static int[] dx = { -1, 1, 2 };
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
K = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
System.out.println(BFS());
}
public static int BFS() {
Queue<Pos> queue = new LinkedList<>();
HashSet<Integer> visited = new HashSet<>();
queue.add(new Pos(N, 0));
visited.add(N);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Pos p = queue.poll();
if (p.x == K) {
return p.moves;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
int newX = (i < 2) ? p.x + dx[i] : p.x * dx[i];
if (isMovable(newX) && !visited.contains(newX)) {
visited.add(newX);
queue.add(new Pos(newX, p.moves + 1));
}
}
}
return -1;
}
public static boolean isMovable(int x) {
if (x < 0 || x > 100000) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
static class Pos {
int x;
int moves;
public Pos(int x, int moves) {
this.x = x;
this.moves = moves;
}
}
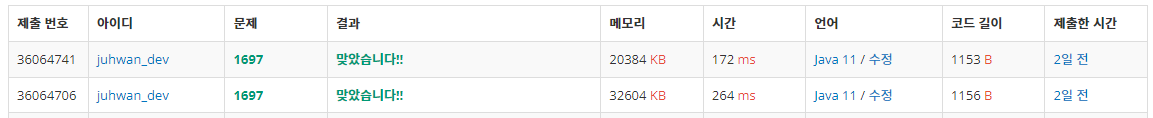
}방문 여부를 판단해야하는 값의 범위가 100,000까지 되다 보니까 HashSet을 이용해서 체크하는 게 더 낫지 않을까 싶어서 이렇게 짜보았다.
결과부터 말하자면 배열쓰는게 더 빠르다. 킁
- 배열 사용
package baekjoon;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class _1697_숨바꼭질 {
static int N, K;
static int[] dx = { -1, 1, 2 };
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
K = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
System.out.println(BFS());
}
public static int BFS() {
Queue<Pos> queue = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[] visited = new boolean[100001];
queue.add(new Pos(N, 0));
visited[N] = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Pos p = queue.poll();
if (p.x == K) {
return p.moves;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
int newX = (i < 2) ? p.x + dx[i] : p.x * dx[i];
if (isMovable(newX) && !visited[newX]) {
visited[newX] = true;
queue.add(new Pos(newX, p.moves + 1));
}
}
}
return -1;
}
public static boolean isMovable(int x) {
if (x < 0 || x > 100000) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
static class Pos {
int x;
int moves;
public Pos(int x, int moves) {
this.x = x;
this.moves = moves;
}
}
}dx를 사용하는 부분만 제외한 일반적인 BFS 코드와 다르지 않다.
newX를 구하는 로직이 마음에 안 들어서 고민했는데 다행히도 한 줄로 해결할 수 있었다.
💡 느낀 점
- 메모리 제한이 빡빡한게 아니고서야... 10만 개 정도는 그냥 배열을 써야겠다는 걸 느꼈다.
- 히든 케이스를 찾을 때는 값 범위의 끝자락에 있는 놈들을 넣어보자...!
반응형
'문제 풀이 > 백준' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 2146번 다리 만들기 (6) | 2021.12.15 |
|---|---|
| 백준 7576번 토마토, 7569번 토마토(3차원 버전) (2) | 2021.12.07 |


댓글